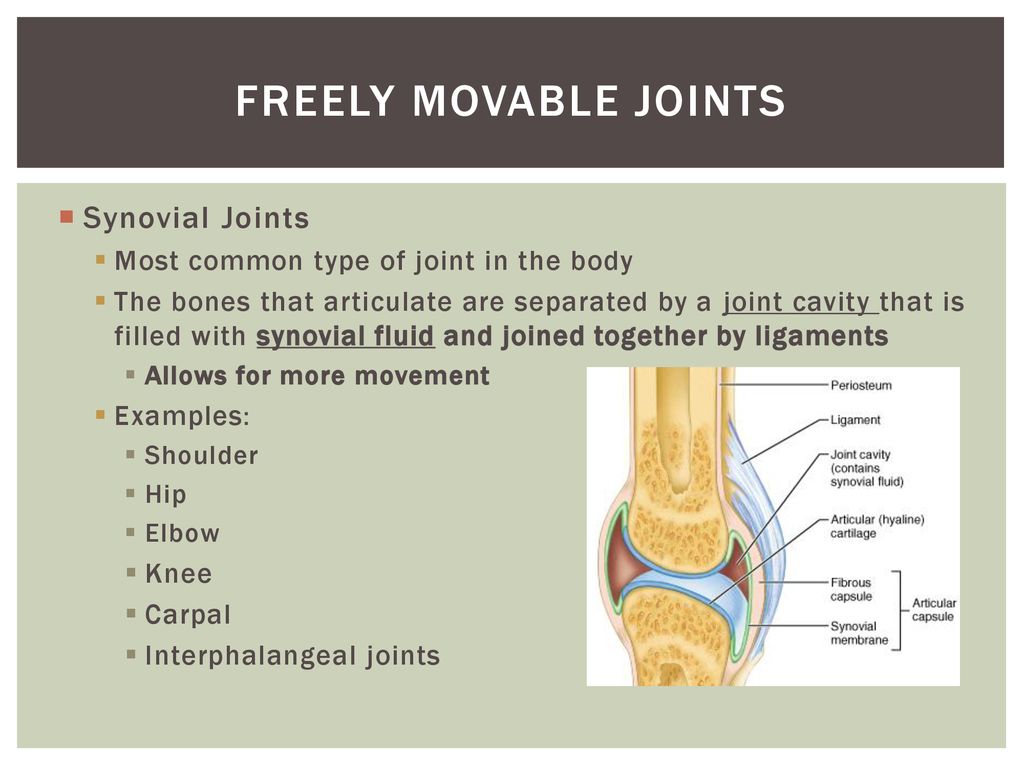
Freely movable joints are joints within the body that can move freely;The slightly movable joint is called amphiarthrosis, which usually allows very little movement at one of the joints Examples of this amphiarthrosis are some of the intervertebral disks present in the spine and also pubic symphysis located in the hip and lower portion of the body Freely Movable These kinds of freely movable joints are known asFreely movable, or synovial (sihNOveeul), joints move in many directions The main joints of the body — such as those found at the hip, shoulders, elbows, knees, wrists, and ankles — are freely movable They are filled with synovial fluid, which acts as a lubricant to help the joints move easily
Anatomy Gross Anatomy Physiology Cells Cytology Cell Physiology Types Of Joints Functional
What are the different types of freely movable joints
What are the different types of freely movable joints-Freely movable The third class of functional joints is said to be freely moving kind of diarthrosis joints Diarthrosis are said to have the highest range of the motion of any kind of joint and also includes the knee, elbow, shoulder and also the wrist Joints are also classified based on the structure of the material present in them What is the most freely movable joint in the body?



Joints Or Articulations Nurse Key
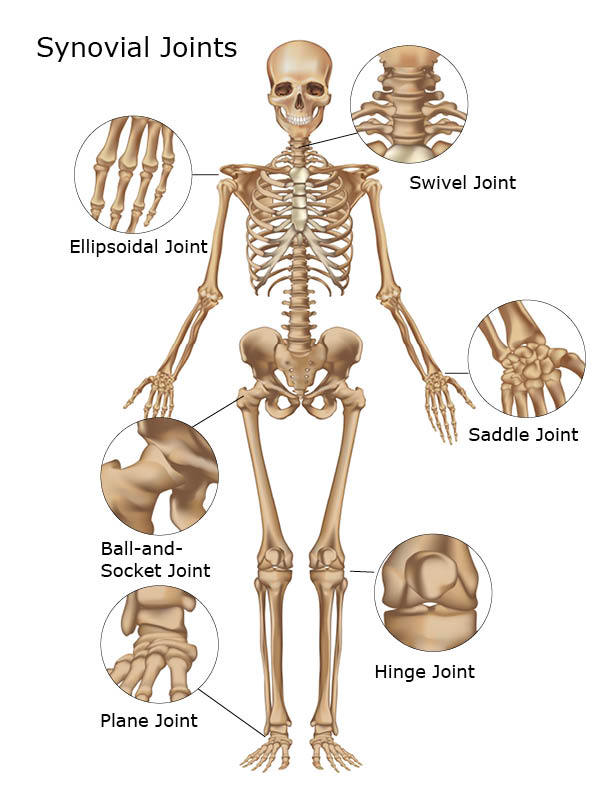
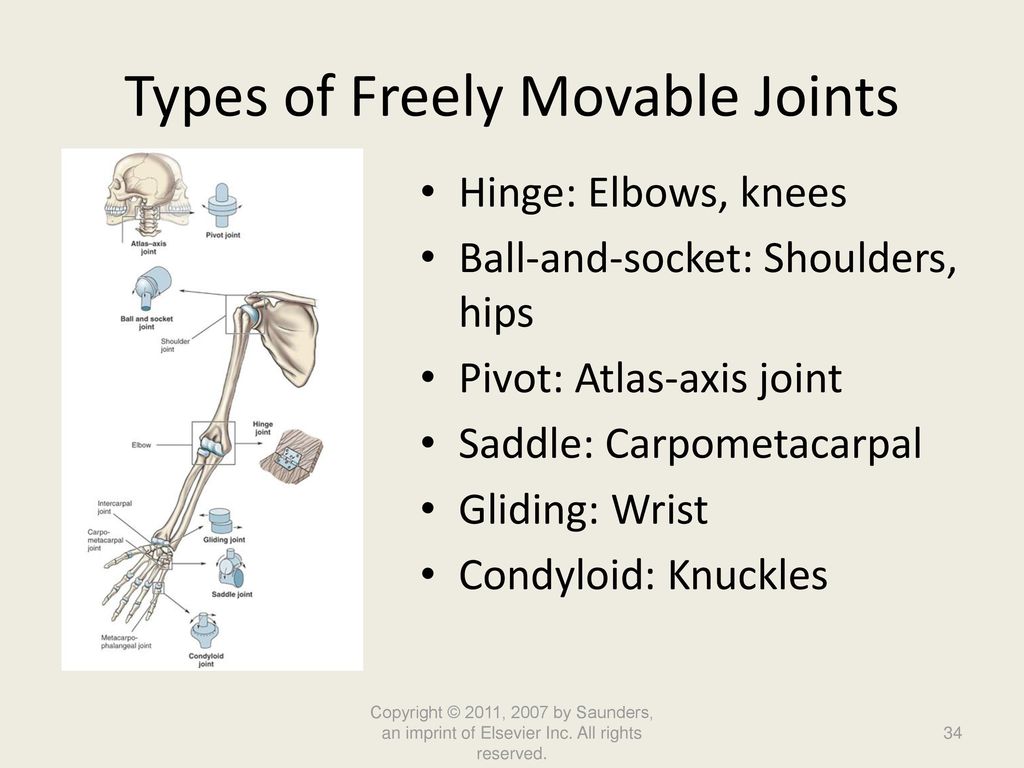
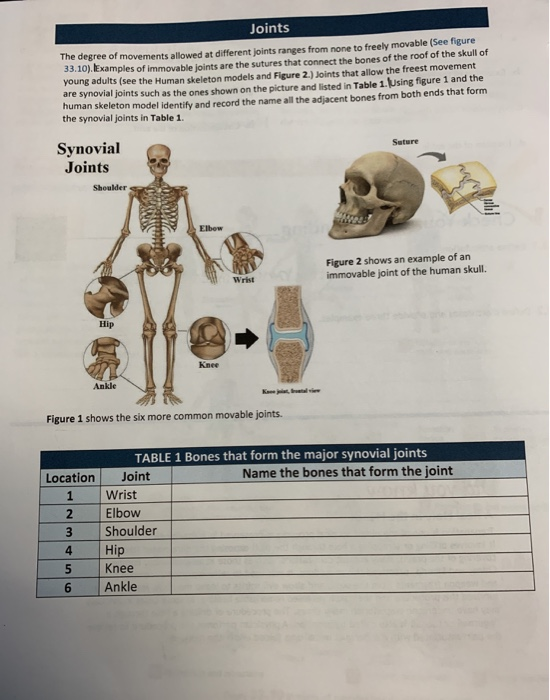
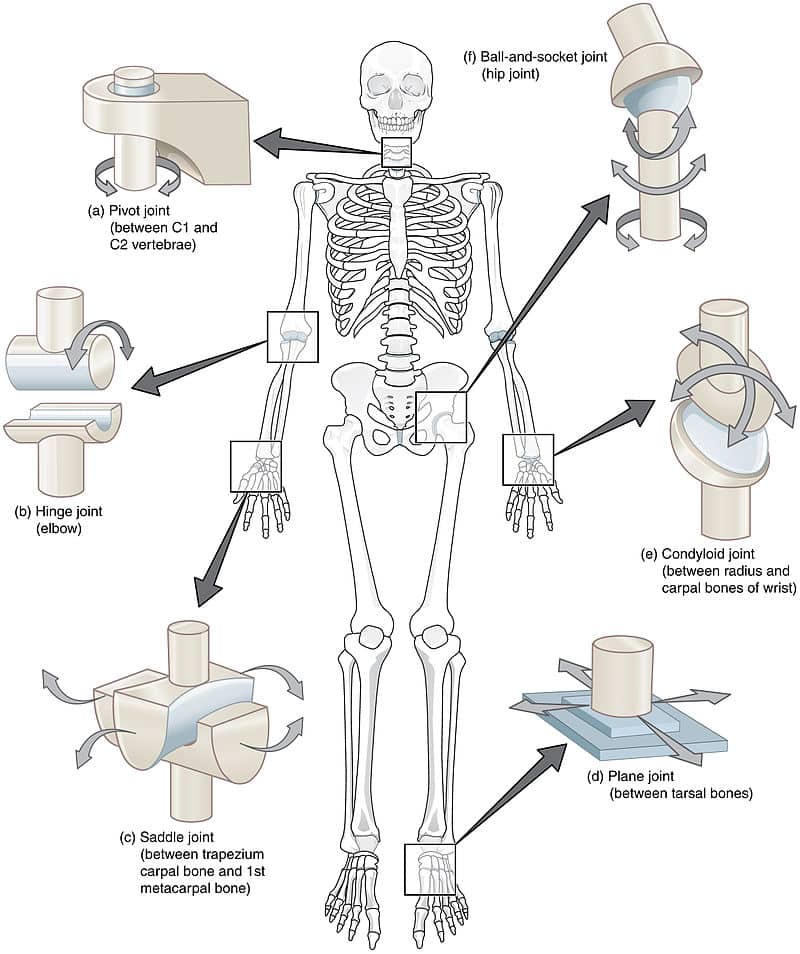
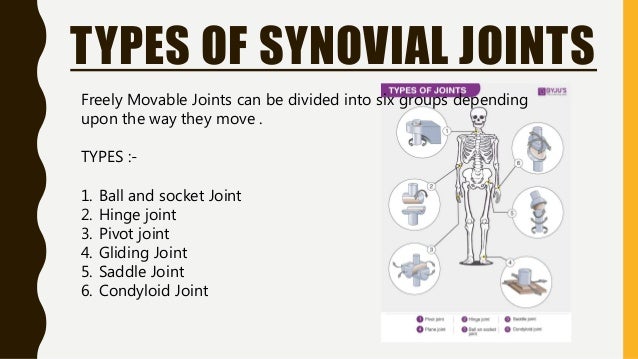
Freely movable (synovial) joints are most abundant and include six types pivot, hinge, condyloid, saddle, plane, and ballandsocket joints There are three types of joints in the body Synovial joints are freely movable and allow for motion at the location where bones meet They provide a wide range of motion and flexibilityJoints The degree of movements allowed at different joints ranges from none to freely movable (See figure 3310) Examples of immovable loints are the sutures that connect the bones of the roof of the skull of young adults (see the Human skeleton models and Figure 2)Start studying bio joints Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools synarthroses example amphiarthroses functional joint that is slightly movable diathroses functional joint that is freely movable shoulder, hip, knee diathroses example types of materials holding the joint together
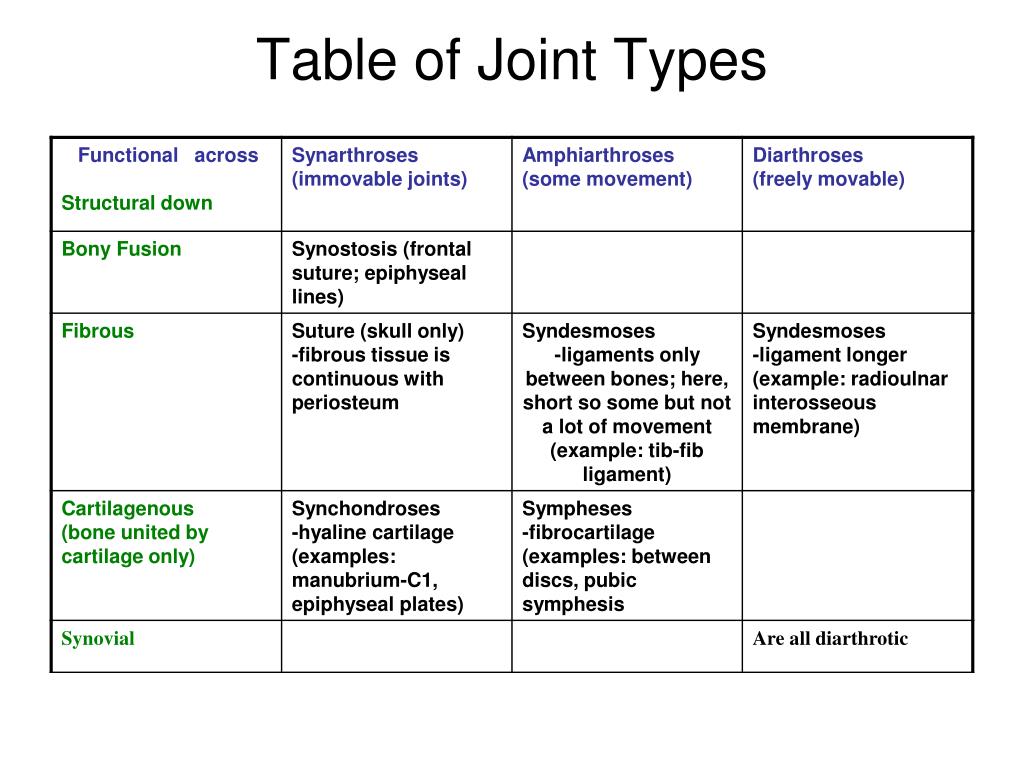
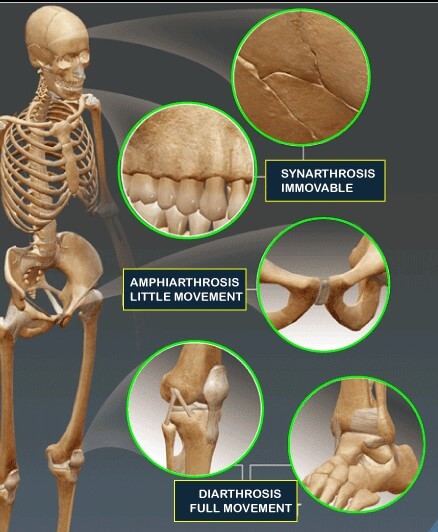
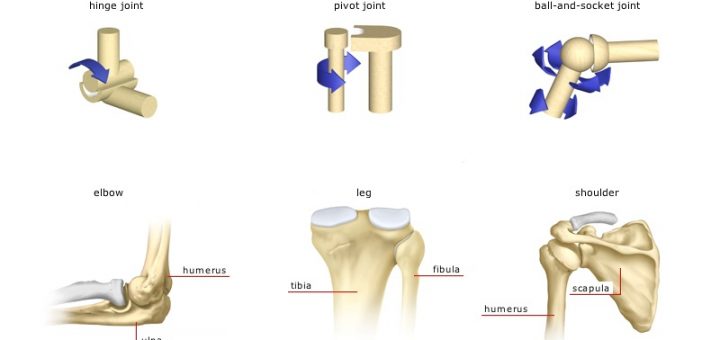
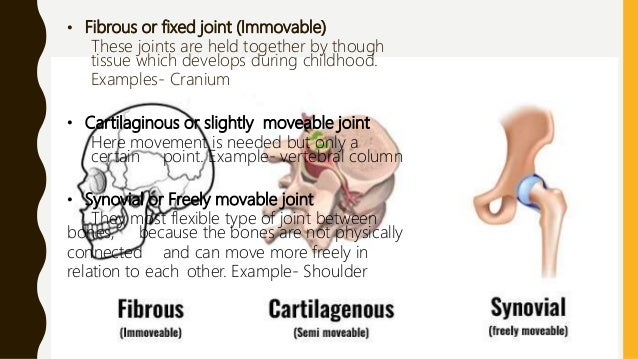
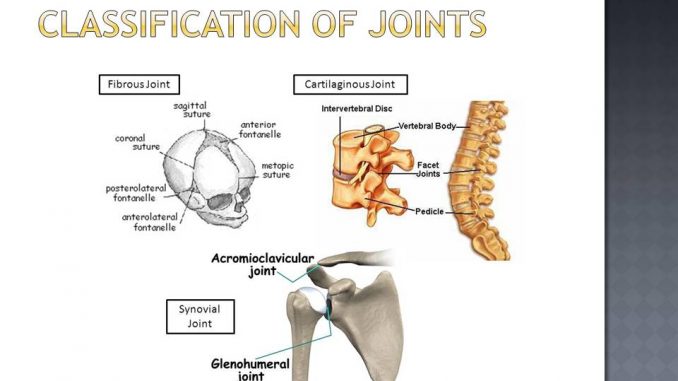
6 different types of synovial joints plane, hinge, pivot, condylar, saddle, ballandsocket Bursae sacs of synovial fluid capable of rolling and decreasing friction where a ligament or other structure would rub against bone;Freely moving joints The six types of freely movable joint include Ball and socket joint – the rounded head of one bone sits within the cup of another, such as the hip joint or shoulder joint Movement in all directions is allowedThe functional classification of joints is determined by the amount of mobility found between the adjacent bones Joints are thus functionally classified as a synarthrosis or immobile joint, an amphiarthrosis or slightly moveable joint, or as a diarthrosis, which is a freely moveable joint (arthroun = "to fasten by a joint")
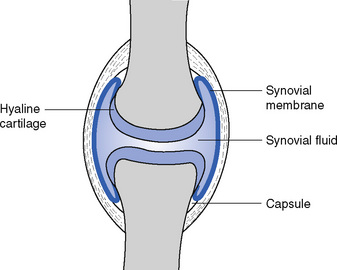
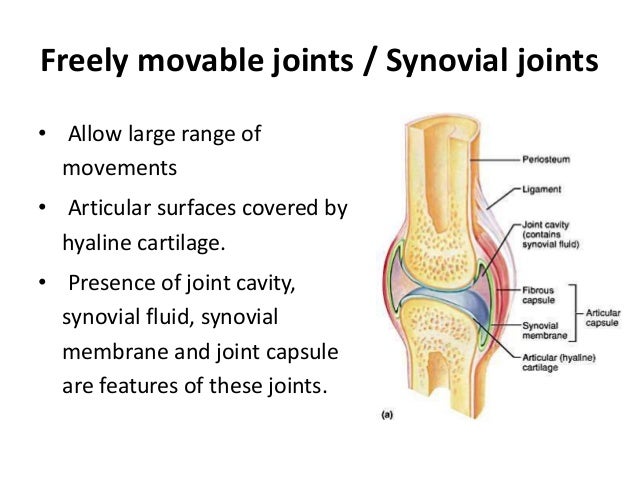
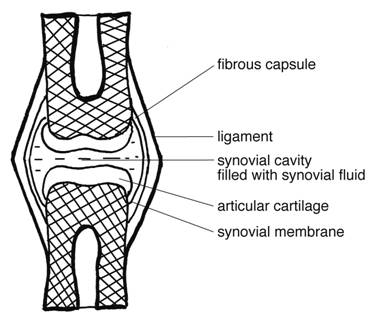
Examples are the symphysis pubis and the costochondral joints of the ribs with the sternum Diarthrodial Diarthrodial joints, also known as synovial joints, are freely movable A sleevelike covering of ligamentous tissue known as the joint capsule surrounds the bony ends forming the joints Freely Movable Joints Most articulations are freely movable The structure of a freely movable joint, or diarthrosis (diarthro 'sis), is more complex These joints are also called synovial (si no'veal) joints The ends of the bones forming the joint are bound together by an articular, or joint, capsuleSynovial joints, also known as movable joints, refer to the joints that are capable of moving in a variety of directions (allow mobility) Such examples include the knee joints, elbow joints, wrist joints, shoulder joints, hip joints and ankle joints The joint surfaces are smooth, covered with cartilage, and gathered in a so called joint capsule



1



3
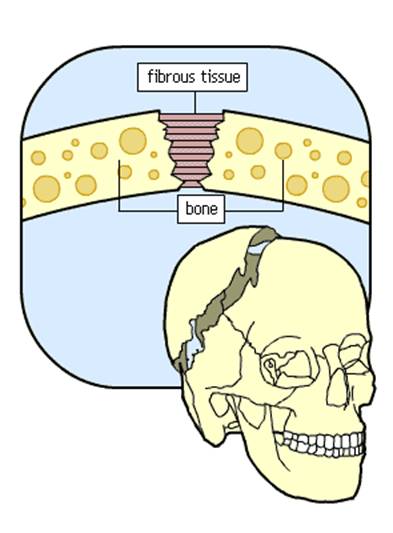
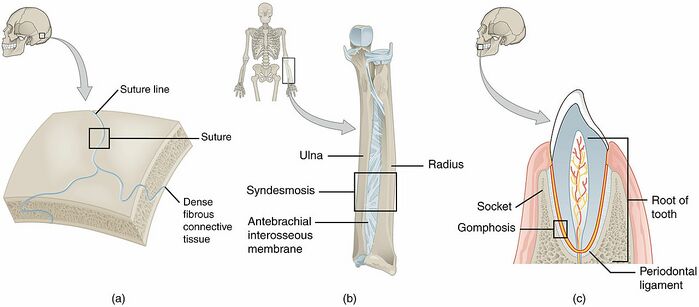
Synovial joints are the freely movable joints that make up most of the joints in the body for voluntary movement It has articular cartilage from hyaline cartilage that covers the ends of bones Joints are classified into three classes on the basis of movabiliyThese three classes areimmovable joints,partially movable joints and freely movable joints Immovable joints These joints doesn't permit movement and the bones are articulated by tough fibrous tissueExamples of such bones are sutural bones etcThey are also called SynarthrosesAssociated with synovial joints but not part of joint Tendon sheaths




Where Two Bones Interconnect Joints Approximately 230 Movable And Semi Movable Joints The Structure Of A Joint Determines The Type And Amount Ppt Download



Unit 1 Types Of Joints Ppt Video Online Download
Synovial joints are flexible, movable, can slide over one another, rotatable and so on These joints are found in our shoulder joint, neck joint, knee joint, wrist joint, etc Functional classification of joints Functional classification of joints is based on the type and degree of movement permittedSection 1 Joint Structure and Movement Learning Outcomes 81 Contrast the major categories of joints, and explain the relationship between structure and function for each category Describe the basic structure of a synovial joint, and describe common accessory structures and their functions Describe how the anatomical and functional • Partly Movable Joints – Partly movable joints allow for slight movement These types of joints are mostly cartilaginous Examples of these joints can be found between the vertebrae, ribs, and sternum • Movable Joints – Movable joints allow the bones to be completely mobile and move freely All movable joints are synovial



Ppt Joints Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Ppt How Are Bones Held Together Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
An amphiarthrosis is a slightly moveable joint, such as the pubic symphysis or an intervertebral cartilaginous joint A diarthrosis is a freely moveable joint These are subdivided into three categories A uniaxial diarthrosis allows movement within a single anatomical plane or axis of motion The elbow joint is an example Diarthroses (freely movable) Also known as synovial joints, these joints have synovial fluid enabling all parts of the joint to smoothlySynovial joints are freely movable An example of plane joint is carpal bones in the The slightly rounded end of the bone perfectly fits into the end of Sports Injuries Physical Therapy For example, the knee joint is the point of connection between the The most common joints are freely movable joints



Anatomy Gross Anatomy Physiology Cells Cytology Cell Physiology Types Of Joints Functional



Fibrous Or Fixed Joints
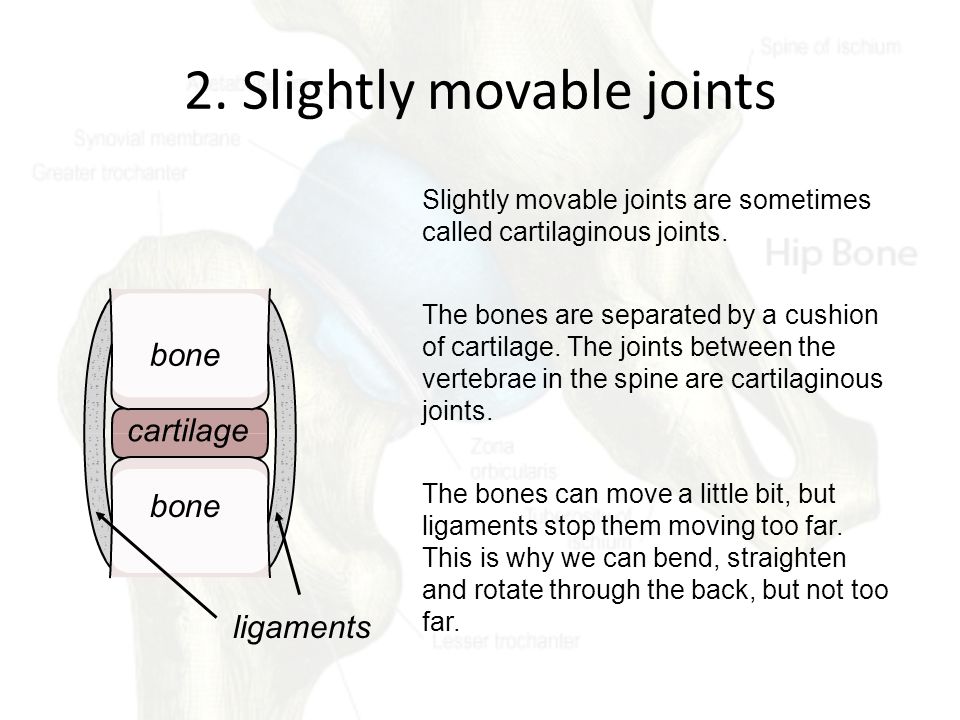
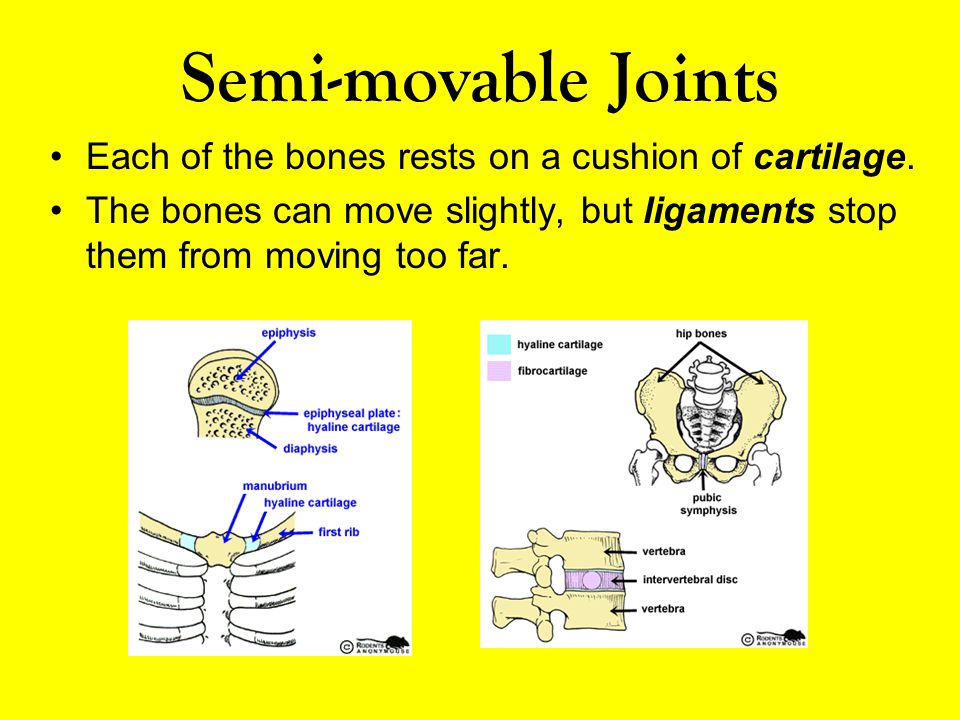
2 Slightly Moveable Joints The bones at a slightly moveable joint can only move a little they are held together by strong straps called ligaments and are joined by protective pads known as cartilage, eg the ribs 3 Freely Moveable Joints At a freely moveable joint the bones move freelyA diarthrosis is a freely moveable joint These are subdivided into three categories A uniaxial diarthrosis allows movement within a single anatomicalImmovable joints allow no movement because the bones at these joints are held securely together by dense collagen The bones of the skull are connected by immovable joints Movable joints allow the most movement



Skeletal System Skeleton Bones Joints Cartilage Ligaments Bursae



The Human Body In Health And Illness 4th Edition Ppt Download
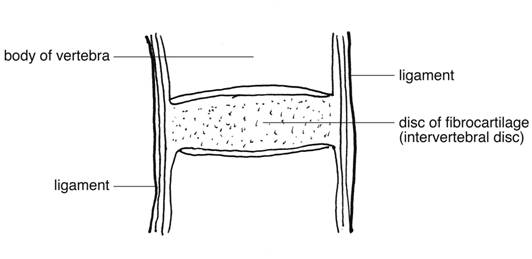
Freely movable joints come in different shapes and allow different movements Six types of freely movable joints exist The ballandsocket joint, of which the shoulder is an example, has a ballshaped head and allows the widest range of motion The elbow is a hinge joint and is able to move in only one plane An example of a synchondrosis is the joint between the diaphysis and epiphysis of a growing long bone Symphyses Symphysial joints are where the bones are united by a layer of fibrocartilage They are slightly movable (amphiarthrosis) Examples include the pubic symphysis, and the joints between vertebral bodies An example is the manubriosternal joint or the joints between the skull bones surrounding the brain An amphiarthrosis is a slightly moveable joint, such as the pubic symphysis or an intervertebral cartilaginous joint A diarthrosis is a freely moveable joint Subsequently, question is, what has Amphiarthrotic and Synarthrotic examples?



Anatomy Gross Anatomy Physiology Cells Cytology Cell Physiology Types Of Joints Functional



Joints Ms Gallagher S Classroom
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsBecause they can move freely, but only within a limited range of motion based on the type of diarthrosis Lastly, a synchondrosis is an example of a joint where you don't think a joint Examples of synchondroses include joints between the ribs and sternum Symphyses examples are the joints in the intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis Synovial Joints Synovial joints are diarthroses, or freely movable joints The structure of synovial joints is more complex than fibrous or cartilaginous joints



Joints Ball And Socket Joint And Pivotal Joints Youtube



Joints And Movements
Most joints in the adult body are diarthroses, or freely movable joints The singular form is diarthrosis The singular form is diarthrosis In this type of joint, the ends of the opposing bones are covered with hyaline cartilage, the articular cartilage , and they are separated by a space called the jointDestination page number Search scope Search Text Search scope Search TextFreely movable Explanation These type of joints also called the diarthrosis are covered with the synovial fluid The synovial fluid acts as a lubricant to prevent friction between the joints as they move If there was no lubrication, friction would cause wear and tear in the joints during movement




Joint Wikipedia



13 13 Skeletal System Joints Biology Libretexts
An amphiarthrosis is a slightly moveable joint, such as the pubic symphysis or an intervertebral cartilaginous joint A diarthrosis is a freely moveable joint These are subdivided into three categories A uniaxial diarthrosis allows movement within a single anatomical plane or axis of motion The elbow joint is an exampleA joint is a point in the body where bones meet They make movement possible by making the skeleton flexible The main bones that form the joints include the following Synovial joints knee, wrist, shoulder, elbow, ankle, and hip joints (freely movable) Semimobile joints articulation of the spine (restricted flexibility)Example skull and tooth joint 2 Cartilaginous joint The two bones are joined together with the help of a disc or pad of white fibrous cartilage Example sternum, ribs, vertebral column, etc 3 Synovial joint These are freely movable joints which allow movement in one or more directions



Types Of Joints Javatpoint




Bones Joints
Synovial joint What is the difference between movable and immovable joint?An example is the manubriosternal joint or the joints between the skull bones surrounding the brain An amphiarthrosis is a slightly moveable joint, such as the pubic symphysis or an intervertebral cartilaginous joint A diarthrosis is a freely moveable jointImmovable Joints 1 It is also called synarthrosis or fixed or fibrous joint 2 Synovial cavity is absent, eg sutures of skull ADVERTISEMENTS Movable Joint 1 It is also called diarthrosis or synovial joint




Pin By Little Colleen On Ccmt Synovial Joints Joints Anatomy Anatomy




What Are Some Examples Of Movable Joints Quora
Freely movable* joint Knee, elbow, phalanges, and so on *Diarthrosis joints are ?freely movable,? Most joints in the adult body are diarthroses, or freely movable joints The singular form is diarthrosis The singular form is diarthrosis In this type of joint , the ends of the opposing bones are covered with hyaline cartilage, the articular cartilage, and they are separated by a space called the joint cavityFreely movable, or synovial (pronounced sihNOveeul), joints move in many directions The main joints of the body — such as those found at the hip, shoulders, elbows, knees, wrists, and ankles — are freely movable They are filled with synovial fluid, which acts as a lubricant to help the joints move easily




What Is The Function Of The Human Skeleton A Plus Topper
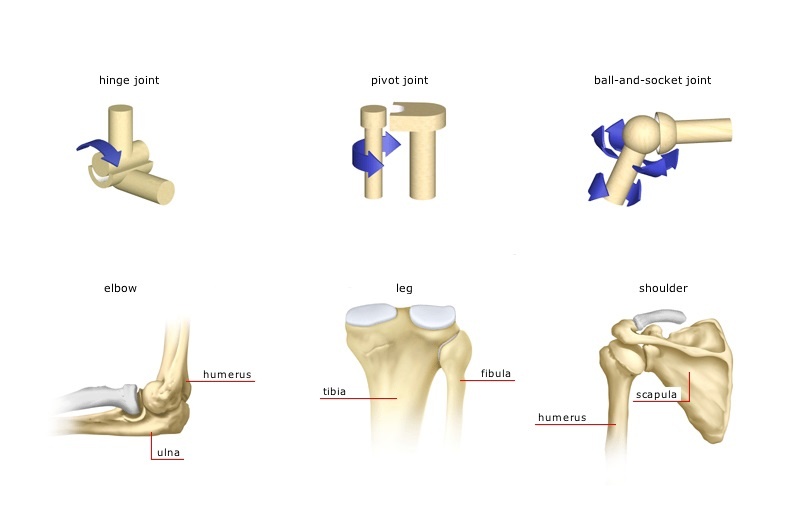



The Joints And Their Significance To The Movement Science Online
Slightly movable joints are also known as cartilaginous joints or amphiarthrosis joints These types of joints are formed by bones that are connected by cartilage The joints are only slightly movable and cannot rotate or move freely Joints can be classified on the basis of structure or functionOther examples of slightly movable joints include the symphysis pubis, the sacroiliac joint, and the joint in the lower leg between the distal ends of the tibia and fibula FREELY MOVABLE JOINTS Most joints within the skeletal system are freely movable, and they have more complex structures than immovable or slightly movable onesThe whole purpose of these joints is to allow for free motion while still See full answer below




Joints 1 Joints For Edexcel 1 2 5




Level 2 Exercise And Fitness Knowledge 4 Joints Amac Training
Movable joints include the shoulder Some specific examples of this type of joint includes the elbow and shoulder joints The elbow is a hinge joint that allows movement in a single plane On the other hand, the shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint that __ acts as a joint lubricant in freely movable joints Synovial fluid The pads of fibrocartilage between the articulating surfaces of teh knee are called __ menisci The fluid filled sacs sometimes associated with freely movable joints are called __ bursae The sacroiliac joint is an example of a __ slightly movable joint Articular cartilage
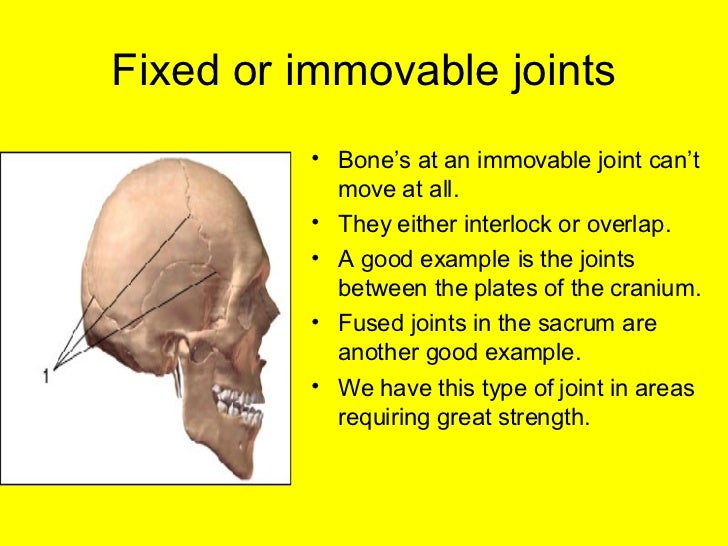



L10a Different Kinds Of Joints
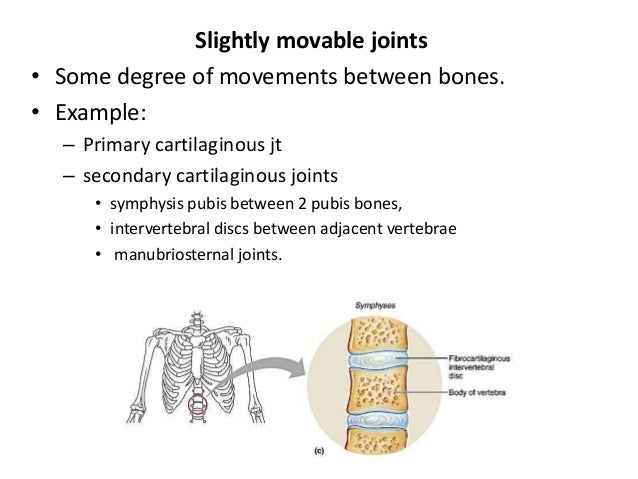



Joints And Movements




Classification Of Joints Anatomy And Physiology I
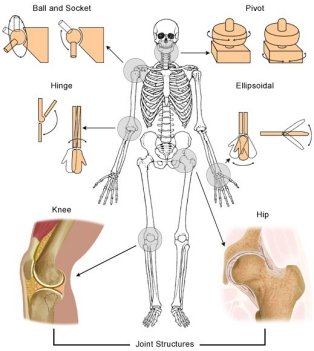



Joint




Joints Or Articulations Nurse Key




Skeletal Movements Movements At Freely Movable Joints Diarthroses Or Synovial Joints U22 Types Of Movement U13 Based On Reference To Person In The Course Hero




Slides Show




Anatomyskeletal System Types Of Joints And Joints Structures




The Skeletal System 8646 C Introduction The Skeletal



Human A P




Slides Show



Joints



Joints The Degree Of Movements Allowed At Different Chegg Com



Classification Of Joints Fibrous Joints Cartilaginous Joints Synovial Joints Teachmeanatomy
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/types_of_synovial_joints-5b6f001e4cedfd00251806ae.jpg)



The 3 Types Of Joints In The Body




Joint




Ppt Joints Of The Human Body Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Joints Definition Classification And Importance Of Joints




The Types Of Joints And Movement Flashcards Quizlet




Joints Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation



Joint Classification Physiopedia




Joints And Mcqs Classification Of Joints Synovial Joints Notes For Neet Gpat Nursing Exam Gpatindia Pharmacy Jobs Admissions Scholarships Conference Grants Exam Alerts
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/synovial_joint-5b6efd4c46e0fb00253e4c5e.jpg)



The 3 Types Of Joints In The Body




Joints Definition Types And Classification Of Joints Videos




Joints Definition Types And Classification Of Joints Videos



6 Types Of Freely Movable Joints



Freely Movable Joints Science Online




What Is A Movable Joint With Pictures



Synarthrodial Joint Definition Of Synarthrodial Joint By Medical Dictionary



Skletal System




Chapter 8 Joints Diagram Quizlet
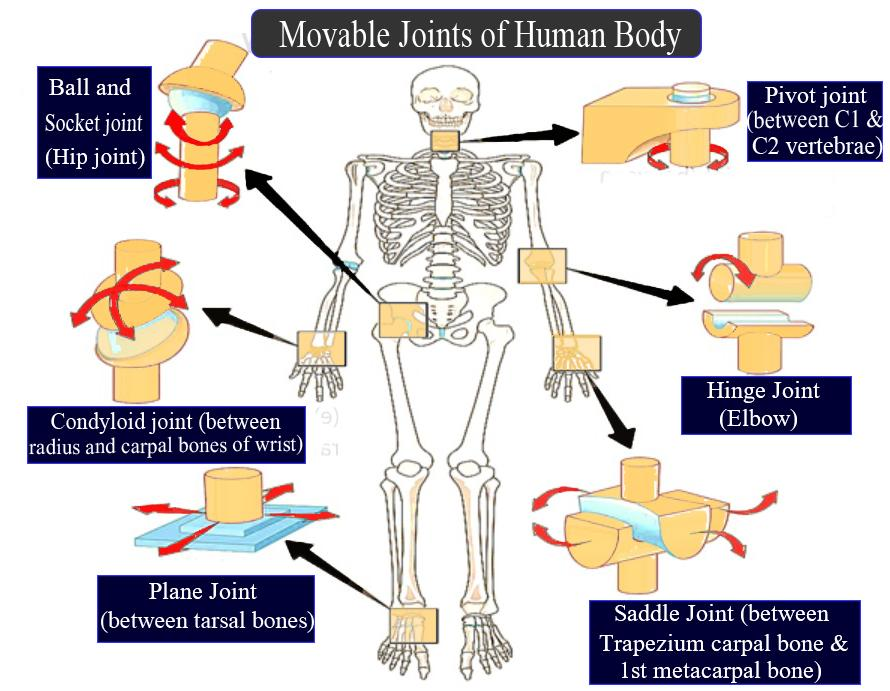



Explain Any Five Movable Joints With Examples Class 11 Biology Cbse




Miracle Pharmacist Today Quiz Joint




Slides Show




Ppt Joints Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 428




The Six Types Of Synovial Joints Examples Definition Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Difference Between Slightly Movable Joints And Immovable Joints Brainly In




6 Types Of Freely Movable Joints
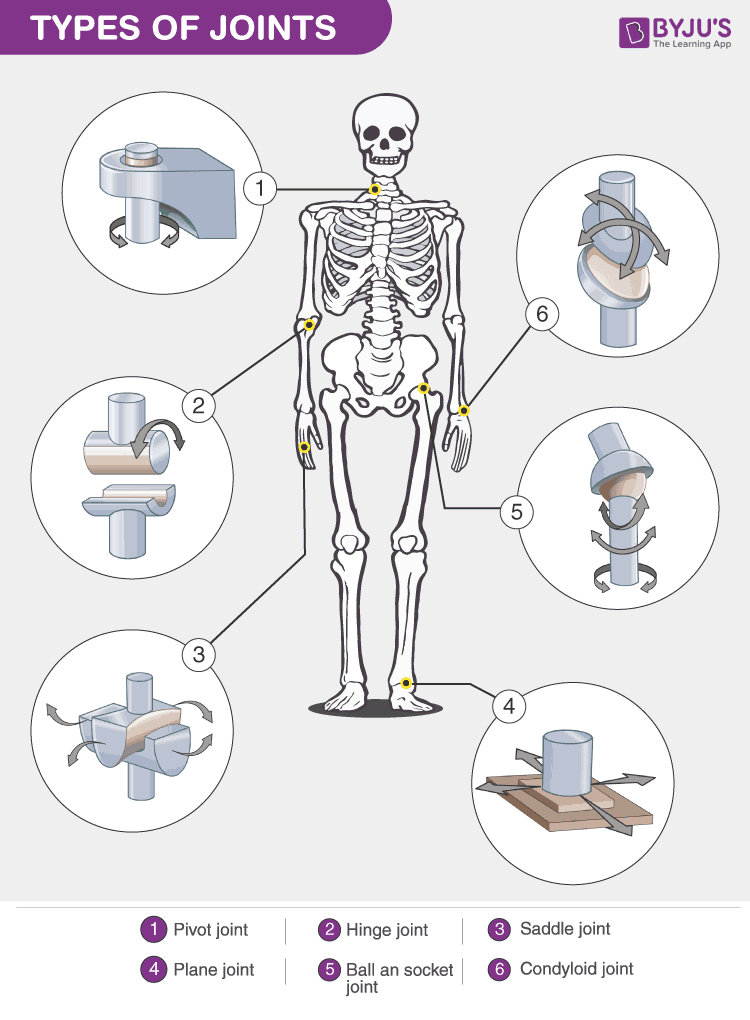



Types Of Joints Classification Of Joints In The Human Body




Arthrology Dr Archana Rani Associate Professor Department Of




Learning Objectives To Gain Knowledge And Understanding Of The Different Types Of Joints In The Body And To Learn Their Structure To Explain The Movement Ppt Video Online Download
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/skull_sutures-5b6ef3d946e0fb002cc029cc.jpg)



The 3 Types Of Joints In The Body



Http Www Lamission Edu Lifesciences Alianat1 Chap 6 joints Pdf



Joints And Movements




What Are Freely Movable Joints Study Com



Movement In Animals Class 6 Science Lesson



1




What Lubricates The Freely Movable Joint At The Shoulder



Skletal System



Joints Of The Human Body Ppt Video Online Download



Topic 1 Anatomy Ib




Joints Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation




Level 2 Exercise And Fitness Knowledge 4 Joints Amac Training



Joints




Joint Series Pic 1 Gulshan Physiotherapy Center Facebook



Joints Ms Gallagher S Classroom




Joints Joints In Human Body Human Body Lesson Plans Joint



Http Www Lamission Edu Lifesciences Alianat1 Chap 6 joints Pdf




Joints Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation



What Are The Two Types Of Movable Joints
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/lumbar_vertebrae-5b6ef83e46e0fb005025872a.jpg)



The 3 Types Of Joints In The Body




Joint Students Britannica Kids Homework Help



Classification Of Joints Online Biology Notes




What Are Examples Of Slightly Moveable Joints Quora



1




Ks 4 Physical Education Joints Tendons And Ligaments




Joints And Its Types Definition Examples Diagrams



Study Notes
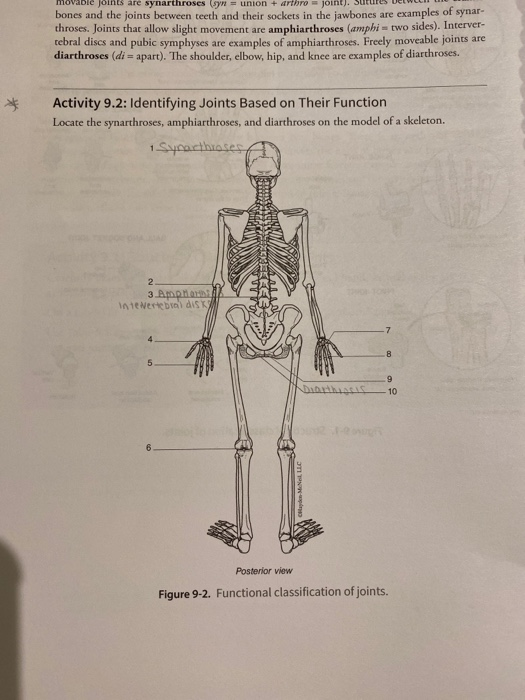



Ble Joints Are Synarthroses Syn Union Arthro Chegg Com




6 Freely Movable Joints By Martin Wren



5 4 Different Kinds Of Joints




Svastham 24 7 Type Of Joints For More Information Facebook
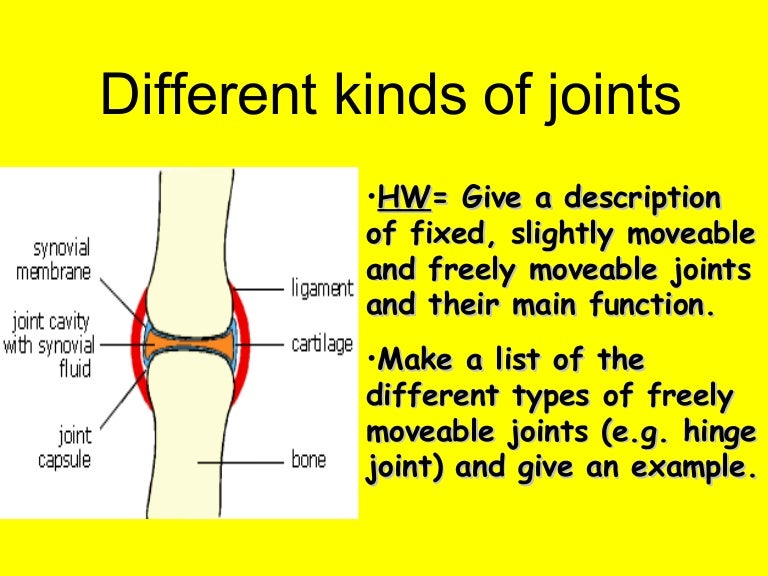



L10a Different Kinds Of Joints




Skeletal System Skeleton Bones Joints Cartilage Ligaments Bursae
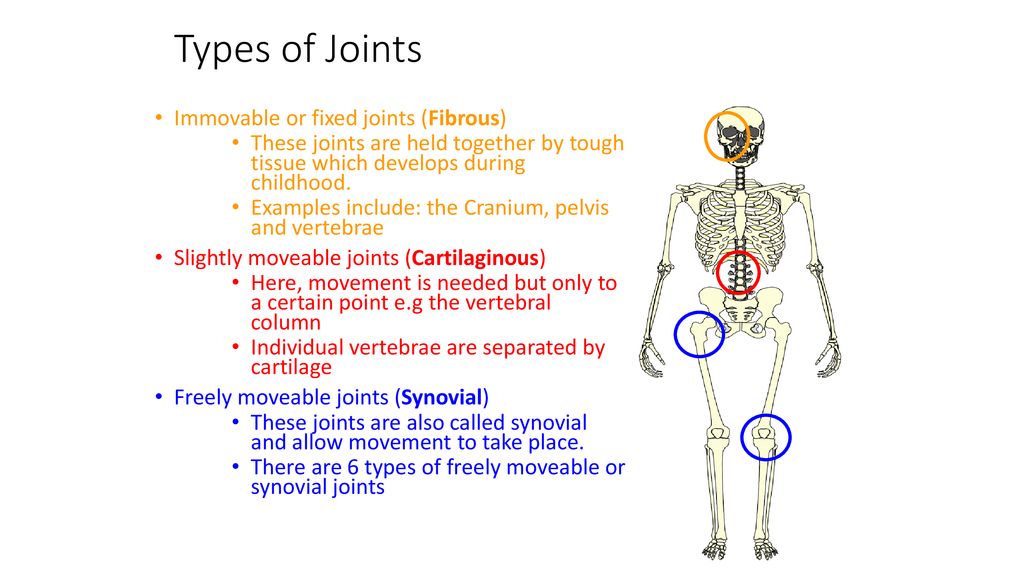



Joints And Movement Unit 4 Skeletal System Ppt Download
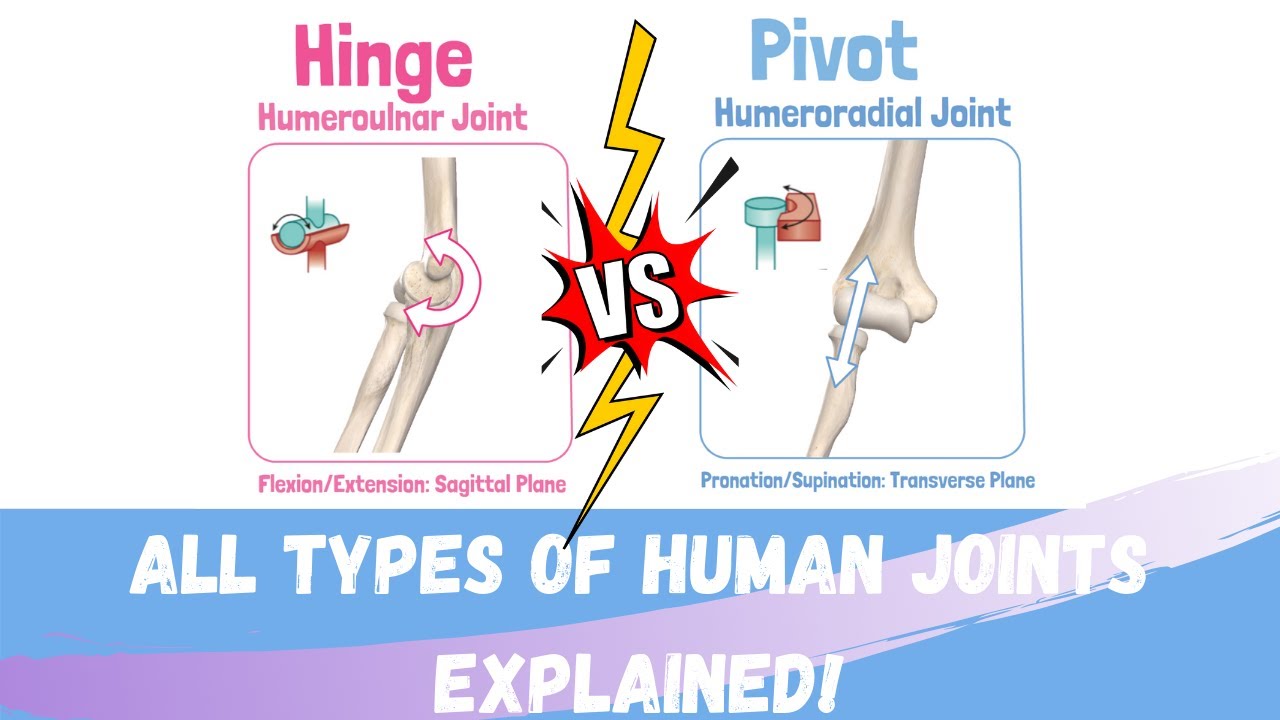



Joint Classification Physiopedia
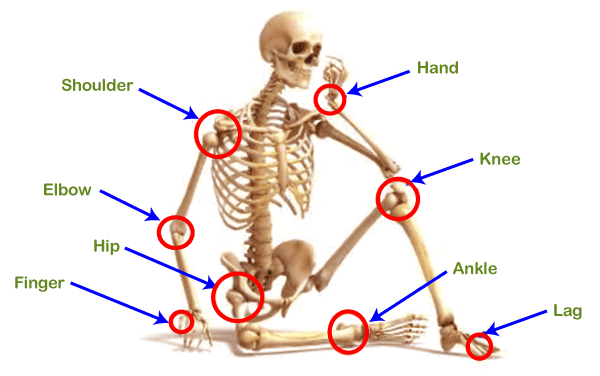



Types Of Joints Javatpoint




Introduction To Medical Terminology 1st Edition Page 36 52 Of 512




Joints Presentation By Lalit M Tiwari Introduction In
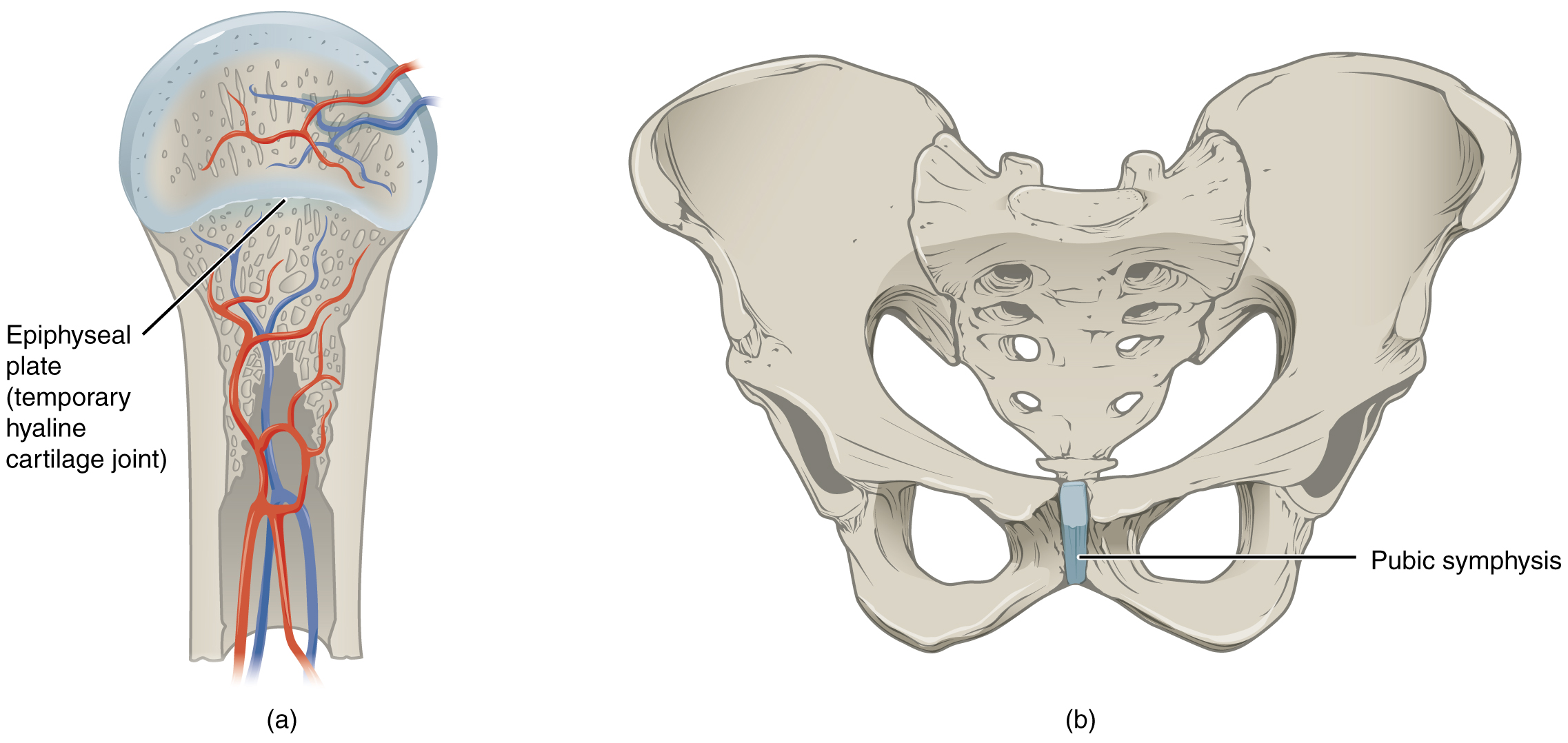



Cartilaginous Joint Wikipedia



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿